Plants on Plants?
Plants on Plants?
In asexual reproduction, one parent organism produces offspring without meiosis and fertilization. Because the offspring inherit all their DNA from one parent, they are genetically identical to each other and to their parent.
There are many different types of organisms that reproduce by asexual reproduction, including fungi, bacteria, protists, plants, and animals.
Fission
Recall that prokaryotes have a simpler cell structure than eukaryotes. A prokaryote’s DNA is not contained in a nucleus. For this reason, mitosis does not occur and cell division in a prokaryote is a simpler process than in a eukaryote.
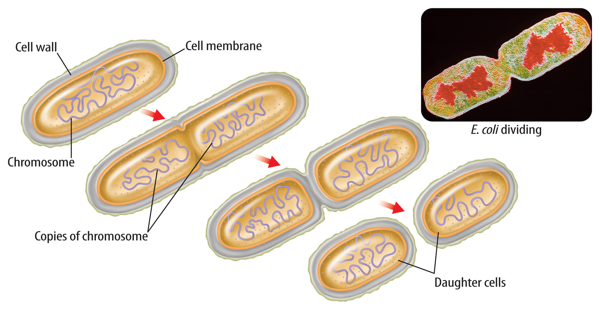
Cell division in prokaryotes that forms two genetically identical cells is known as fission.
Cell division in prokaryotes that forms two genetically identical cells is known as fission.
Fission begins when a prokaryote’s DNA molecule is copied. Each copy attaches to the cell membrane. Then the cell begins to grow longer, pulling the two copies of DNA apart. At the same time, the cell membrane begins to pinch inward along the middle of the cell. Finally the cell splits and forms two new identical offspring. The original cell no longer exists.
As shown in Figure 1, E. coli, a common bacterium, divides through fission. Some bacteria can divide every 20 minutes. At that rate, 512 bacteria can be produced from one original bacterium in about three hours.
Mitosis Cell Division
Many unicellular eukaryotes reproduce by mitotic cell division. In this type of asexual reproduction, an organism forms two offspring through mitosis and cell division. In Figure 2, an amoeba’s nucleus has divided by mitosis. Next, the cytoplasm and its contents divide through cytokinesis and two new amoebas form.
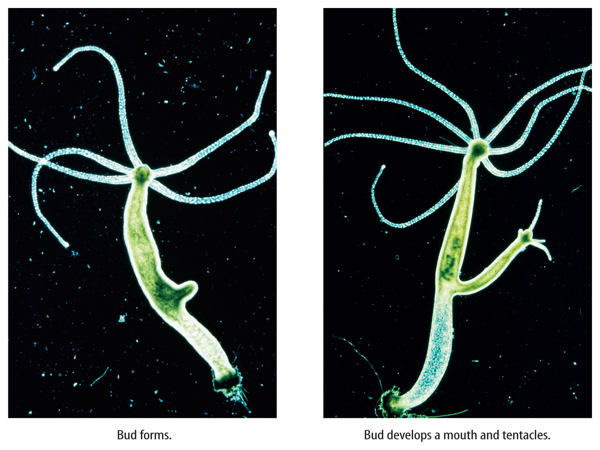
In budding, a new organism grows by mitosis and cell division on the body of its parent. The bud, or offspring, is genetically identical to its parent. When the bud becomes large enough, it can break from the parent and live on its own. In some cases, an offspring remains attached to its parent and starts to form a colony.
Figure 3 shows a hydra in the process of budding. The hydra is an example of a multicellular organism that can reproduce asexually. Unicellular eukaryotes, such as yeast, can also reproduce through budding, as you saw in the Launch Lab.
Figure 3 shows a hydra in the process of budding. The hydra is an example of a multicellular organism that can reproduce asexually. Unicellular eukaryotes, such as yeast, can also reproduce through budding, as you saw in the Launch Lab.
Aninal Regeneration
Another type of asexual reproduction, regeneration, occurs when an offspring grows from a piece of its parent. The ability to regenerate a new organism varies greatly among animals.
Producing New Organisms Some sea stars have five arms. If separated from the parent sea star, each arm has the potential to grow into a new organism. To regenerate a new sea star, the arm must contain a part of the central disk of the parent. If conditions are right, one five-armed sea star can produce as many as five new organisms.
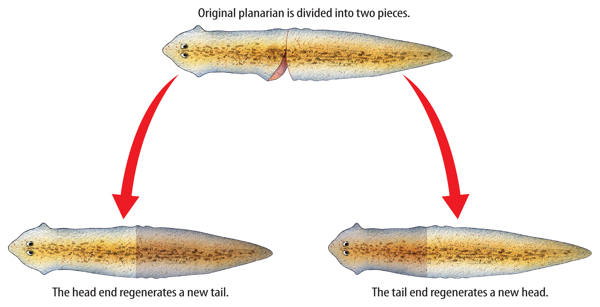
Sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sponges, and planarians, such as the one shown in Figure 4, can also reproduce through regeneration. Notice that each piece of the original planarian becomes a new organism. As with all types of asexual reproduction, the offspring is genetically identical to the parent.
Producing New Parts When you hear the term regeneration, you might think about a salamander regrowing a lost tail or leg. Regeneration of damaged or lost body parts is common in many animals. Newts, tadpoles, crabs, hydra, and zebra fish are all able to regenerate body parts. Even humans are able to regenerate some damaged body parts, such as the skin and the liver. This type of regeneration, however, is not considered asexual reproduction. It does not produce a new organism.
Vegetative Reproduction
Plants can also reproduce asexually in a process similar to regeneration. Vegetative reproduction is a form of asexual reproduction in which offspring grow from a part of a parent plant.
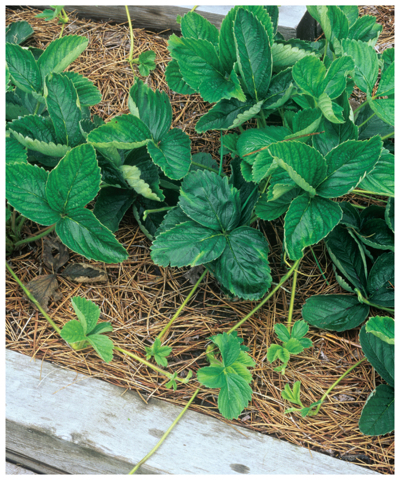
For example, the strawberry plants shown in Figure 5 send out long horizontal stems called stolons. Wherever a stolon touches the ground, it can produce roots. Once the stolons have grown roots, a new plant can grow—even if the stolons have broken off the parent plant. Each new plant grown from a stolon is genetically identical to the parent plant.
For example, the strawberry plants shown in Figure 5 send out long horizontal stems called stolons. Wherever a stolon touches the ground, it can produce roots. Once the stolons have grown roots, a new plant can grow—even if the stolons have broken off the parent plant. Each new plant grown from a stolon is genetically identical to the parent plant.
Vegetative reproduction usually involves structures such as the roots, the stems, and the leaves of plants. In addition to strawberries, many other plants can reproduce by this method, including raspberries, potatoes, and geraniums.
Cloning
Fission, budding, and regeneration are all types of asexual reproduction that can produce genetically identical offspring in nature. In the past, the term cloning described any process that produced genetically identical offspring. Today, however, the word usually refers to a technique developed by scientists and performed in laboratories.
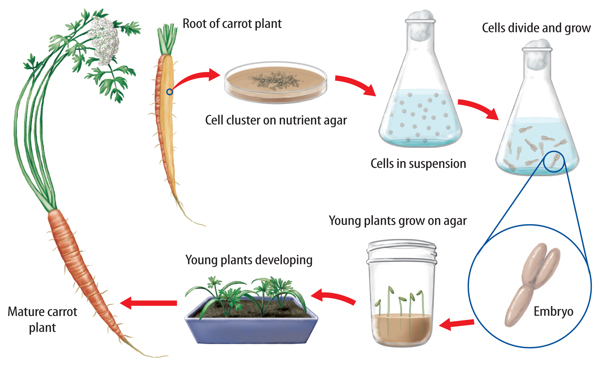
Cloning is a type of asexual reproduction performed in a laboratory that produces identical individuals from a cell or from a cluster of cells taken from a multicellular organism. Farmers and scientists often use cloning to make copies of organisms or cells that have desirable traits, such as large flowers.
Cloning is a type of asexual reproduction performed in a laboratory that produces identical individuals from a cell or from a cluster of cells taken from a multicellular organism. Farmers and scientists often use cloning to make copies of organisms or cells that have desirable traits, such as large flowers.
Figure 6 New carrot plants can be produced from cells of a carrot root using tissue culture techniques.
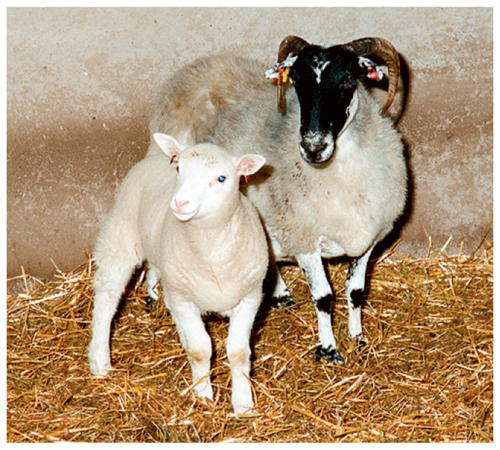
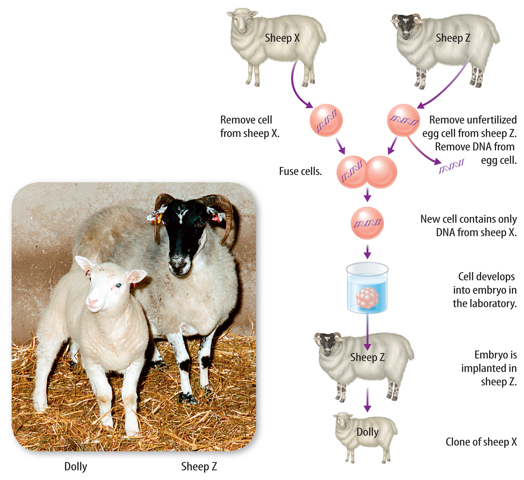
Animal Cloning In addition to cloning plants, scientists have been able to clone many animals. Because all of a clone’s chromosomes come from one parent (the donor of the nucleus), the clone is a genetic copy of its parent. The first mammal cloned was a sheep named Dolly. Figure 7 illustrates how this was done.
Scientists are currently working to save some endangered species from extinction by cloning. Although cloning is an exciting advancement in science, some people are concerned about the high cost and the ethics of this technique. Ethical issues include the possibility of human cloning. You might be asked to consider issues like this during your lifetime.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
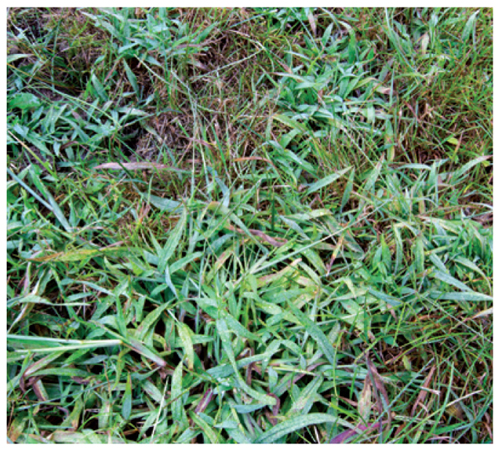
What are the advantages to organisms of reproducing asexually? Asexual reproduction enables organisms to reproduce without a mate. Recall that searching for a mate takes time and energy. Asexual reproduction also enables some organisms to rapidly produce a large number of offspring. For example, the crabgrass shown in Figure 8 reproduces asexually by underground stems called stolons. This enables one plant to spread and colonize an area in a short period of time.
\
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
Although asexual reproduction usually enables organisms to reproduce quickly, it does have some disadvantages.
Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to their parent. This results in little genetic variation within a population.
Why is genetic variation important? Recall that genetic variation can give organisms a better chance of surviving if the environment changes. Adaptation is possible.
Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to their parent. This results in little genetic variation within a population.
Why is genetic variation important? Recall that genetic variation can give organisms a better chance of surviving if the environment changes. Adaptation is possible.
Another disadvantage of asexual reproduction involves genetic changes, called mutations, that can occur. If an organism has a harmful mutation in its cells, the mutation will be passed to asexually reproduced offspring. This could affect the offspring’s ability to survive.
Lesson Review
Visual Summary
Lesson Assessmen14.B
Use Vocabulary
1. In ________ ________, only one parent organism produces offspring.
2. Define the term cloning in your own words.
3. Use the term regeneration in a sentence.
Understand Key Concepts
4. State two reasons why asexual reproduction is beneficial.
5. Which is an example of asexual reproduction by regeneration?
A.cloning sheep
B.lizard regrowing a tail
C.sea star arm producing a new organism
D.strawberry plant producing stolons
6. Construct a chart that includes an example of each type of asexual reproduction.
7. Tissue culture is an example of which type of reproduction?
A.budding
B.cloning
C.fission
D.regeneration
8. Which type of asexual reproduction is shown in the figure below?
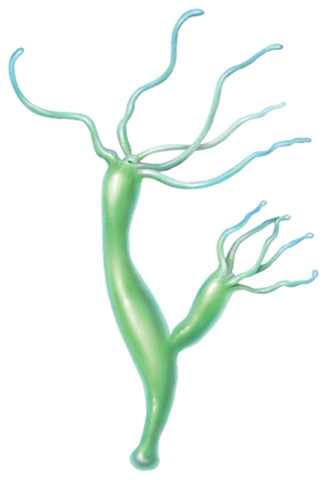

A.budding
B.cloning
C.fission
D.regeneration
9. A bacterium can reproduce by which method?
A.budding
B.cloning
C.fission
D.regeneration
Interpret Graphics
10. Examine the diagram below and write a short paragraph describing the process of tissue culture.
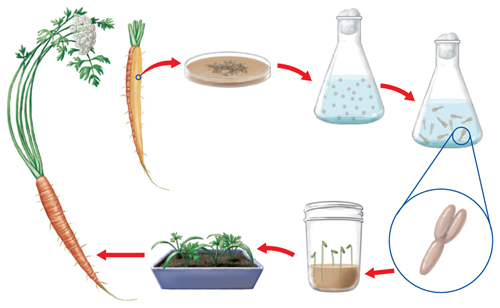

11. Organize Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to list the different types of asexual reproduction that occur in multicellular organisms.



Bill Coster/Getty Images